KPIs to Measure Warehouse Performance and Efficiency

Time to read: 15 minutes
It is difficult to imagine a prosperous e-commerce business without a warehouse—a space that stores products for stocking, packing, and shipping preparation before they are distributed or sold.
Multiple supply chain representatives, from manufacturers and wholesalers to distributors and third-party logistics providers, use warehouses. Each of these representatives should use warehouse KPIs to maximize the efficiency of the warehousing process.
This article will help you dive deeper into the warehousing concept and learn more about the top 22 warehouse KPIs that you should measure.
Understanding the Warehousing Process
As we have mentioned, a warehouse is a place where businesses store and manage their inventory. Thus, warehousing is a critical component of any e-commerce supply chain because it directly affects the safety and security of stored goods, their timely delivery, and customer satisfaction.
Research shows that 67% of businesses believe that running out of stock after an order is placed (i.e., overselling) is the top inventory mistake that leads to lost customers. Therefore, you should have a comprehensive approach to manage your warehousing processes, which includes the following activities:
- Employing warehouse management and providing training
- Setting up your warehouse properly and using modern equipment
- Building strong relationships with reliable suppliers
- Creating real-time insight into inventory location and quantity
- Forecasting shipping volume and product demand
- Monitoring applicable safety regulations
- Picking, packing, and shipping merchandise effectively
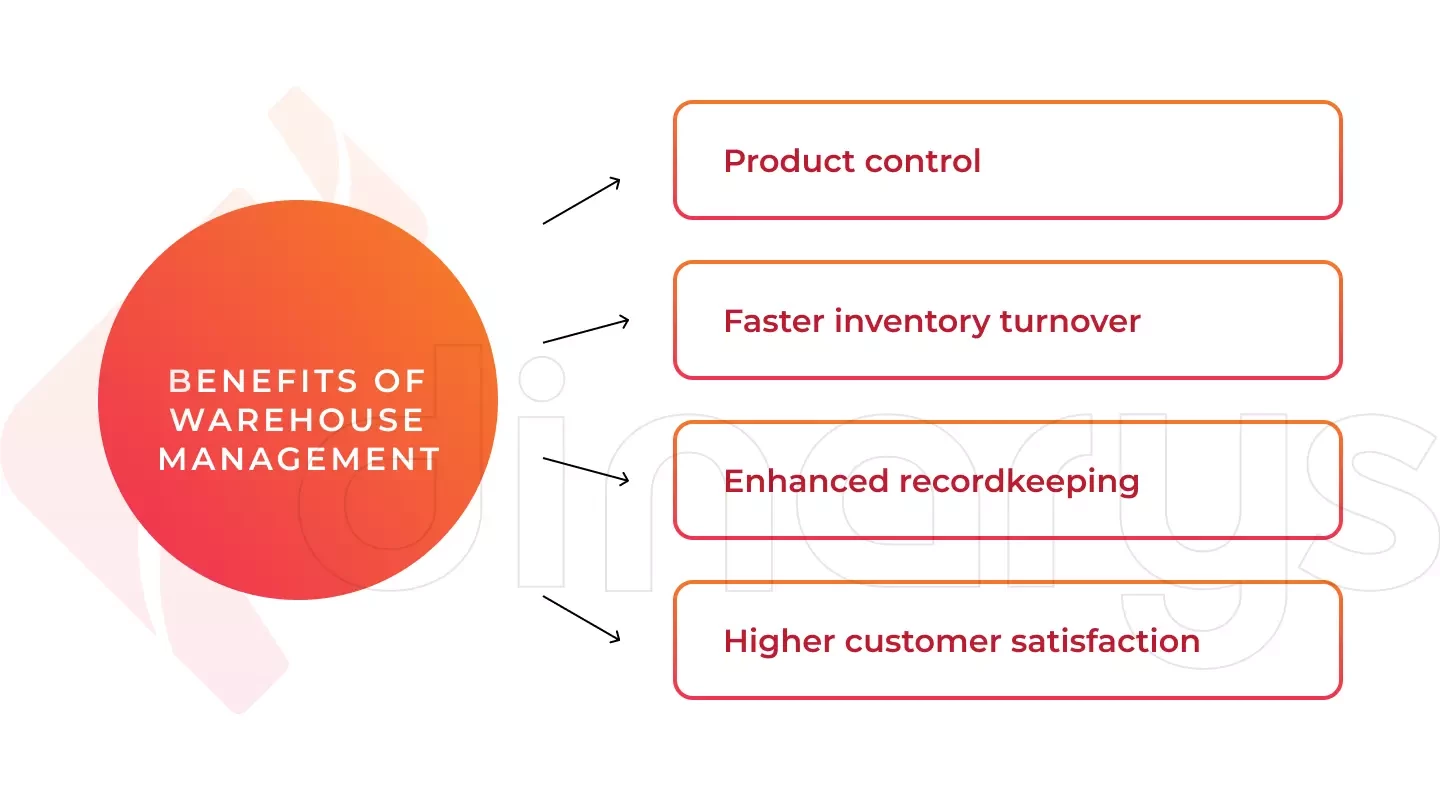
What are the benefits of warehouse management?
Warehouse management provides various advantages for your e-commerce business. By successfully managing your warehouse, you gain the following benefits:
- Product control. Warehousing helps you manage your inventory by tracking and controlling what and when merchandise needs to be shipped.
- Faster inventory turnover. This information reflects the number of times an organization has sold and replaced inventory during a specific time period. Using proper warehousing practices and KPI measurements, you can stock your shelves and get new products onto your shelves more quickly.
- Enhanced recordkeeping. Managing all your inventory in one place allows you to accurately monitor your stock and sales. Furthermore, implementing a warehouse management system provides a complete picture of your inventory, its location, and the type and amount of inventory you need to reorder.
- Higher customer satisfaction. This is the ultimate goal for any entrepreneur because higher customer satisfaction leads to repeat orders and higher profits. By warehousing your inventory, you minimize the possibility that your clients will order a product that is out of stock.
Top 22 Warehouse KPIs
To reap the benefits of your warehousing practices fully, it is imperative that you measure warehouse KPIs. Warehouse KPIs function in different ways, but the majority apply to most warehouses.
This section explains the top 22 warehouse metrics that help you improve the performance of your warehouse and overall business. Depending on your business objectives, you can use all of these metrics or combine some of them.
Inventory KPIs
Inventory KPIs involve any activity that relates to the products you store in your warehouse. These metrics help track the movement of your inventory. To measure the performance of your warehouse inventory management activities, consider using the following KPIs:
- Inventory-to-sales ratio. This measures the amount of inventory in your warehouse compared to the number of sales. You can use this metric to adapt your inventory to high margins. A good inventory-to-sales ratio ranges from 0.167 to 0.25.
- Inventory accuracy. This KPI measures the difference between your warehouse inventory records and your real-time inventory. This KPI is often leveraged to control inventory quality and avoid stockouts and shrinkage.
- Inventory turnover rate. As previously stated, this metric indicates the number of times inventory was sold during a given period. To calculate this metric, divide the cost of goods sold by the average inventory for the same period.
- Inventory shrinkage. This metric reflects the excess amount of inventory identified in the records that no longer exist in the actual inventory. This metric can help businesses identify undesirable situations, such as damage, theft, or supplier fraud.
Lets talk about itHave a project in mind?
Picking KPIs
Tracking picking KPIs helps companies properly configure the picking process, which is the process of selecting the right product after an order has been placed.
- Order-picking accuracy. This metric is a percentage that represents the total number of orders picked and verified as accurate prior to shipment divided by the total number of orders picked during the same period of time.
- Pick-to-ship cycle time. This information captures the number of hours from when an order is released to be picked until the time the order is shipped. This metric includes the time it takes to pick an order, prepare it for shipping, and place it with a carrier.
Distribution KPIs
Distribution KPIs measure the efficiency and performance of the flow of products from the warehouse to the customer. Distribution metrics can be used in addition to other processes, such as channel design management, third-party logistics, fleet management, logistics health and safety, and order picking and shipment.
- Order lead time. This metric reflects the average time it takes for an order to reach the customer once it has been placed. It is a crucial metric for assessing the order management capability of e-commerce companies.
- Perfect order rate. This KPI measures how many orders have been delivered without incident (e.g., damaged goods or late shipments) and assists businesses in achieving their customer-centric goals.
- Rate of return. This information reflects the gain or loss of an investment over a particular period of time. Simply stated, the rate of return is the gain or loss compared to the cost of the initial investment, and it is usually expressed as a percentage. When this KPI is positive, it indicates a gain, and when it is negative, it indicates a loss on the investment.
Receiving KPIs
Receiving inventory is the process of ordering and shipping new inventory to your warehouse or 3PL. The following metrics will assist you in accurately measuring your warehouse receiving activities:
- Receiving efficiency. This KPI indicates the performance of the receiving area. This metric is calculated by dividing the volume of inventory received by the number of hours worked. For example, assume you receive 5,000 items per week and have five employees who each work 40 hours. Your receiving efficiency would be 25 items per hour (5,000 ÷ 200 = 25). The lower the number, the more efficient your receiving capacity is.
- Cost of receiving per line. This metric is the cost of receiving a line item on a purchase order. This metric can be calculated by dividing the total cost of receiving by the total number of line items. The higher the number, the less efficient your receiving process is.
- Receiving cycle time. This information indicates the average time used to process the received inventory, which includes accounting, sorting, and storing it. This metric is calculated by dividing the total time spent sorting received stock by the total number of received items.
Put-Away KPIs
In warehousing, put-away processes include all activities that occur between receiving goods from suppliers and putting them away in their assigned places. Evaluating the put-away metric enhances storing activities, reduces the risk of misplacing or losing items, and keeps your warehouse organized. Some beneficial put-away KPIs include the following:
- Put-away cost per line. This metric is the same as the receiving cost per line but measures the cost to put away a line item on a purchase order. The higher the put-away cost per line, the less efficient the put-away process is.
- Put-away accuracy rate. This metric represents the proportion of items that were put away correctly the first time. A value of 1 indicates that no errors occurred. This rate is calculated by dividing the total cost of put-away by the total number of line items.
- Put-away cycle time. This information reflects the speed at which put-away activities occur. It is the total time used to complete each put-away assignment.
Safety KPIs
Ensuring safety is one of the top priorities in everything you do in the warehouse. By measuring the following metrics, businesses can prevent work-related injuries before they occur.
- Time lost due to injury rate. A lost-time injury (LTI) is an on-the-job injury that results in the loss of productive work time. An injury is considered an LTI when the injured employer is unable to perform regular job tasks or misses time from work for recovery.
- Accidents per year. This metric monitors how many accidents cost time and money during a specific year. Ideally, this number should be zero, but if it is not, it can help you assess the scale of the problem.
- Time since the last accident. Similar to accidents per year, this metric is obvious and is a core indicator of warehouse safety.
- Total recordable incident rate. This parameter reflects the total number of work-related injuries per 100 full-time employees during a specific year.
Cultural KPIs
Cultural KPIs measure the company culture, which reflects how a company treats its employees and how it fosters employee engagement, productivity, and performance.
- Employee turnover rate. This KPI refers to the percentage of employees who leave an organization during a specific period of time. Although employees come and go, a high attrition rate is concerning because it usually indicates problems within your warehouse that require your attention.
- Employee net promoter score (NPS). This warehouse metric indicates employee engagement and loyalty to an organization. This score is often measured as part of a wider study that considers employee satisfaction. The NPS is calculated based on the responses to the following question: On a scale from 0–10, how likely are you to recommend our product/service to your family or friends?
- Manager satisfaction score. Good leadership is an essential element of a strong company culture. Thus, it is crucial to assess manager satisfaction and employee satisfaction. The best way to measure this KPI is to conduct anonymous surveys that ask employees to rate their managers to determine how well they perform their management responsibilities.
Lets talk about itHave a project in mind?
Conclusion
When you own an e-commerce business, you should conduct many activities to ensure that your company performs well. Warehouse management is one of these activities. Paying attention to this process will result in on-time shipping, exceptional customer service, and higher profit margins.
To ensure that your warehousing area performs correctly, it is important to conduct regular assessments using the top warehouse KPIs that we have identified. If you are searching for a digital solution to improve KPIs related to your warehouse and e-commerce, contact Dinarys. As a leading e-commerce software development services company, we know how to digitize your warehouse activities and create a better customer experience.
Let professionals meet your challenge
Our certified specialists will find the most optimal solution for your business.