You need neither cooking skills nor visiting grocery stores to serve dinner today. All you need is a smartphone. We bet you ordered food online this week, didn’t you? Stats suggest that even before the lockdowns about 60% of Americans ordered food delivery at least once a week. When the quarantine restrictions became a norm, food delivery services turned from an additional option into a must-have for the catering sector players.
How to create a food delivery service is not an idle question, therefore. Brick-and-mortar cafes and restaurants have to compete with purely online projects that threaten to occupy the whole food industry while recurring lockdowns add fuel to fire.
Food is the sort of the basic necessity that makes relevant online services evolve dramatically: a delicious menu cannot remain the only decisive factor for customers any longer. There must be various options that provide both fast delivery and unprecedented user experience.
A very wide remit is emerging for the food sector players who are capable of recognizing a clear promise in software development. The developers, in their turn, are armed with numerous technologies that can make literally each food delivery project as unique as effective. Multifaceted web platforms coexist with lightweight mobile apps in the contemporary food delivery segment of the internet. It is up to foodservice providers to choose both the type and scope of their software solutions.
We are going to reveal how a fully-fledged food delivery website can be created with either a framework-based approach or purely custom development. Must-have capabilities, optional features, monetization strategies, development approaches, and estimated costs all constitute the content of the present post. Enjoy reading.
Food Delivery Market Overview
The good news about the food delivery sector is that no single monopolist is available on the market. Of course, there are some leading projects there, but both the competition and continuously growing demand on the market keep enough space for new players. The American market is shared between such famous food delivery services as UberEats, DoorDash, Caviar, GrubHub, and Postmates. Customers from Great Britain prefer Just Eat and Deliveroo mostly. The Chinese food delivery leader is Meituan.
If you have an idea to start a new food delivery service it is never too late. Nearly 13% of the entire US restaurant market was taken up by online food delivery during COVID-19. The trend seems to go on and by 2025, online food delivery is expected to grow to a 21% share of the total restaurant market. The lockdown is just an accompanying factor of growth of the sector that has been thriving as such since 1994. Nothing hints at either slower growth or overcrowded markets anytime soon.

How to Launch a Food Delivery Service
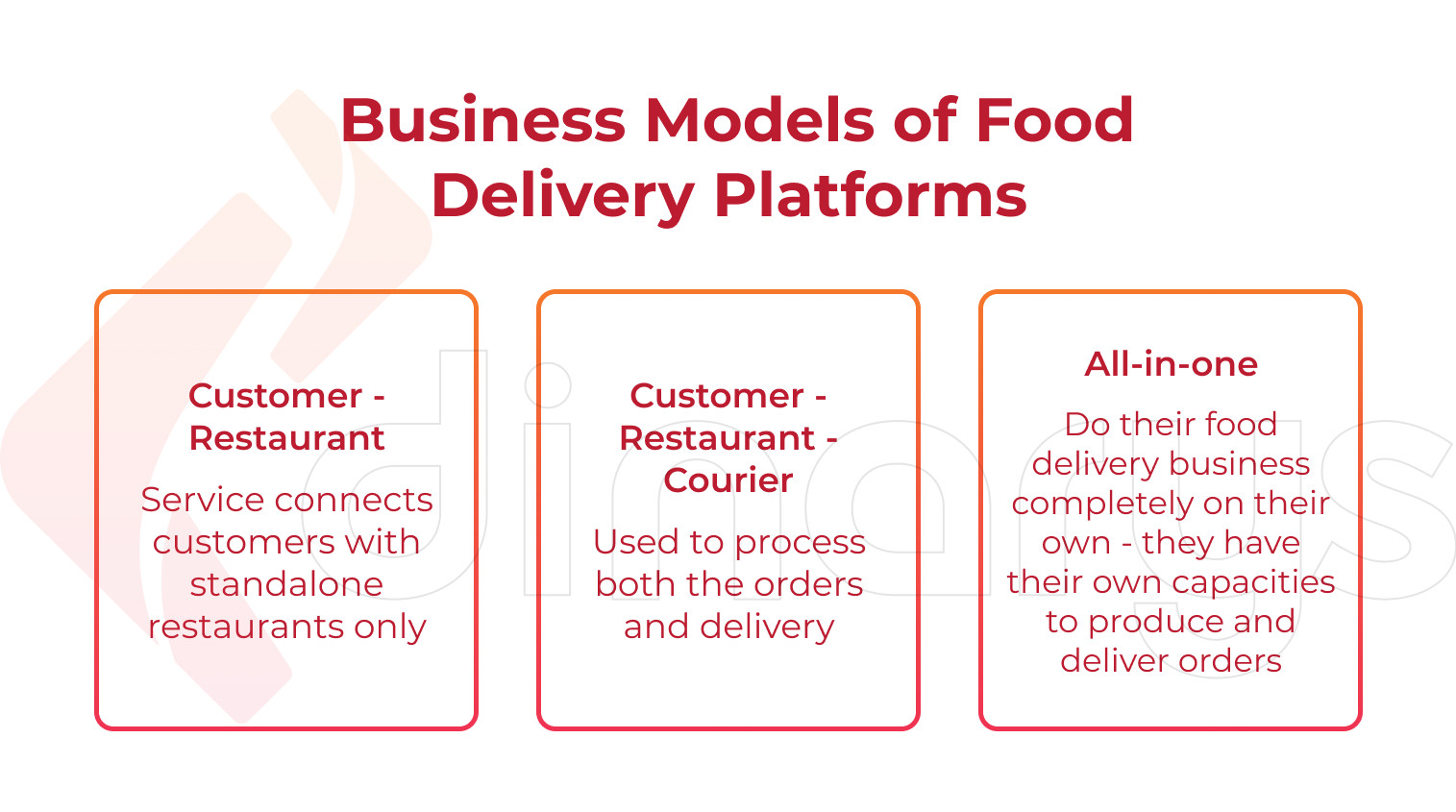
It is worth addressing the issue with the business model of your service to be selected first of all. The commonly accepted model implies making an order via the internet when the ordered food is to be delivered from a restaurant to a customer’s location by a courier. The public at large rarely appreciates the reinvention of the wheel and there is no surprise in the stats saying that 90% of food delivery services over the world work under such a model. Accepting this model for your project is reasonable if you have no experimental innovations to implement in the sector.
By the way, innovative approaches to the food delivery service appear regularly. But they imply changes in some production aspects rather than in business models. For example, the most promising sub-trend in the food delivery industry is the so-called ghost kitchens. This is when a new project starts not from a conventional restaurant with all associated facilities and staff but from a rented premise with the necessary kitchen equipment to produce and pack just food for contactless deliveries.
Whether it is a full-service restaurant or a ghost kitchen you can never establish a food delivery service without a corresponding website having all functionalities related to the business. Hence, the architecture of your online service has to meet the business goals you are going to achieve.
Income-Generating Model
Before you contact software developers to start creating your website you need to choose the income-generating model of your future service. The architecture of your website will directly depend on how you are going to earn money. The general business model mentioned above can bring you income in the following three ways of doing business:
-
Customer - Restaurant: This is when your service connects customers with standalone restaurants only. In other words, your service is a hub between those who order food and those who make orders appear in front of the customer’s door. It means the engaged restaurants (cafes, ghost kitchens, etc) arrange the deliveries on their own. Delivery Hero and Grubhub use such an income-generating model. This is the simplest and oldest way of doing the food delivery business. The engaged restaurants pay 7% - 15% commissions to food delivery platforms of such a sort. One of the best solutions in this context is Zomato.
-
Customer - Restaurant - Courier: Food delivery platforms that use this income-generating model process both the orders and delivery in contrast to the previous model. It seems to be more convenient for the engaged restaurants since they do not need to care about couriers.
The platforms, in turn, have an additional opportunity to earn some money from courier fees: the fixed courier price on the platform can be higher than the actual cost of the courier services contracted by the platform. The critical factor of the model is in the delivery period that should not exceed 30 minutes to keep the ordered food hot and fresh. Caviar, Deliveroo, UberEats, and DoorDash use such an income-generating model in their business.
-
All-in-one: In contrast to both previous models, the all-in-one services do their food delivery business completely on their own. It means they have their own capacities to produce and deliver orders. Hence, the web platform, food production facilities, and couriers all belong to a company of such a sort. This is the most independent type of food delivery business as well as the most expensive one at the same time.
Corporate catering programs are provided by such food delivery services oftentimes since they can arrange well-balanced meals delivered right to the office. It goes without saying that the all-in-one services have to invest a lot in special facilities such as fridges, thermoses, warm food containers, etc. Besides, they should have their own fleet of vehicles (including drones) to provide courier activities. Metabolic Meals is a relevant use case for this income-generating model.
Actually, there is one more income-generating model inherent in large food chains such as KFC and McDonald’s. It can be called Restaurant - Customer where the customer audience is tightly linked to a certain brand. You can hardly order sushi instead of Big Mac from McDonald’s, right? That’s why we leave this model aside since it is more relevant to the restaurant sector rather than to food delivery services.
Monetization Strategy
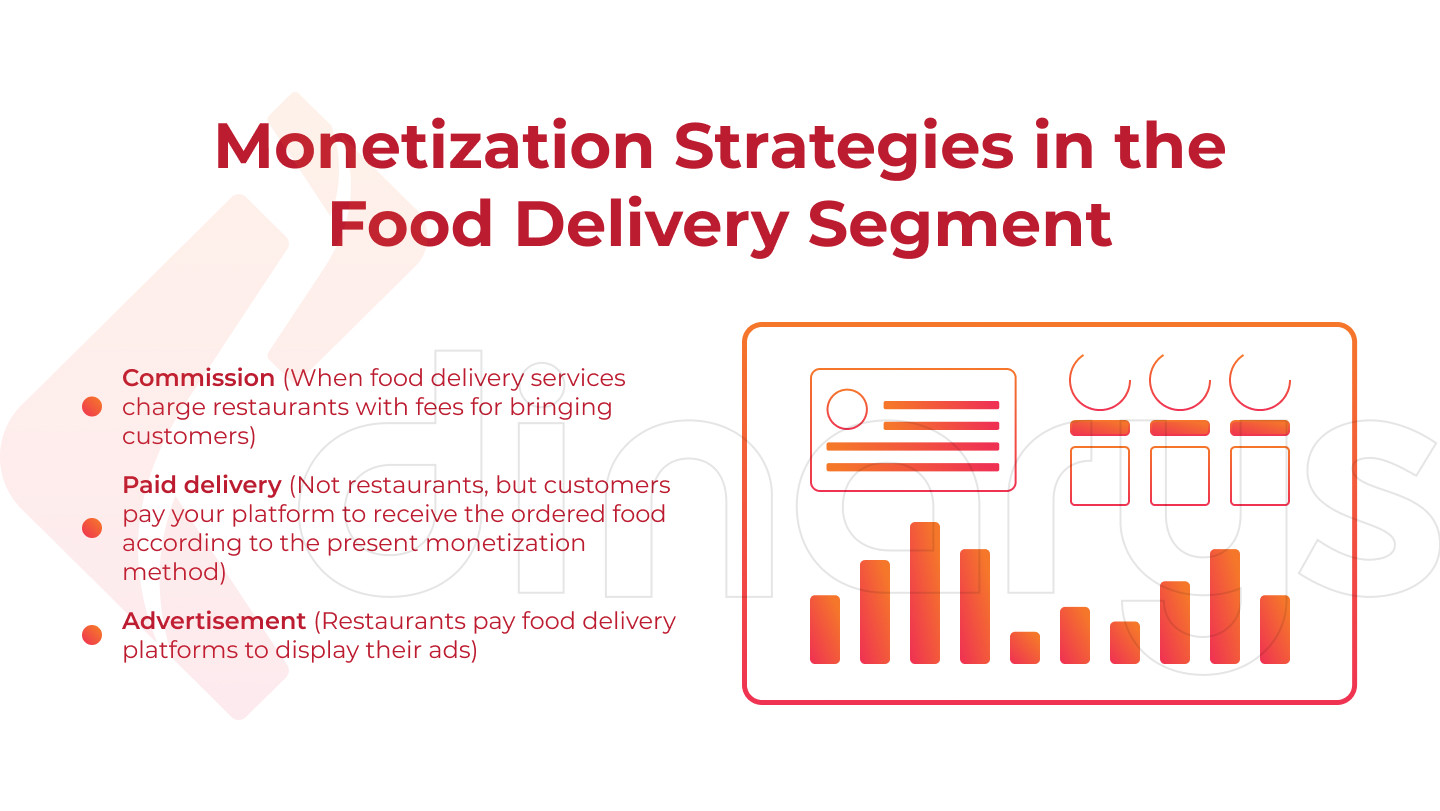
We have to add another classification option you have to select before developing your food delivery website. While the income-generating model determines the scope of your service, the monetization strategy reveals the source of your income. There are three popular monetization strategies in the food delivery segment.
-
Commission: This is when food delivery services charge restaurants with fees for bringing customers. A restaurant pays a platform a certain percentage of the cost of each order received via the platform. UberEats, for example, requires 30% from restaurants for each order while insisting on keeping their prices stable with no increase to cover the fee.
A large commission can be unaffordable for small restaurants and cafes, however. That’s why we suggest you charge local catering vendors a modest percentage for maintaining mutually profitable collaboration: the modest profits can be compensated by the stronger sustainability of your business in such a case. Besides, some other sources of income are always available.
-
Paid delivery: In contrast to the previous strategy, not restaurants, but customers pay your platform to receive the ordered food according to the present monetization method. The strategy makes you either establish your own courier service or focus on collaboration with the available courier delivery vendors. Both the delivery price and the way you add the delivery cost to orders may significantly vary depending on many factors such as destination, order amount, current demand, etc.
The strategy is simpler than the previous one in terms of organizational issues since the number of courier services is usually much smaller than the number of available cafes and restaurants. Being very sustainable as such the strategy alone can unlikely make you rich, however. We recommend considering some additional sources of income to be involved.
-
Advertisement: This is quite a common monetization method for various internet projects, food delivery services are no exception. Your first thought about the strategy implies pop-up windows with ads having nothing in common with food, right? Possibly, but not necessarily. Almost every food delivery website has a main page with a list of recommended restaurants. You can bet they don’t appear in it by accident. They pay food delivery platforms to display their ads. It is a win-win strategy: platforms get profit while restaurants draw new clients.
All monetization strategies have their own pros and cons. But our general advice to all future food delivery providers is to focus not on a single monetization method: there is always an opportunity to create a hybrid solution with multiple income sources.
Why Every Food Delivery Service Needs a Website
No matter whether you are launching a fresh startup or doing a stable restaurant business when a dedicated web platform helps you meet numerous challenges of the food delivery sector. Let’s indicate just a few of them.
- Leaving rivals behind in the internet presence: Millions of people look for cafes and restaurants on Google Maps every day. Only half of those catering providers have their promo pages at best. Where can customers find info about the menus, services, and prices to make a decision to visit the restaurants and/or order takeaway food?
- Getting free promotion from friendly restaurants: This is the ads exchange strategy when you promote restaurants on your website while the restaurants promote your service in response. Such a strategy is especially useful for newly established food delivery services that have just started creating their customer audiences.
- Automating your customers’ orders: It seems to be obsolete to drop paper leaflets in nearby post boxes and wait for calls from customers. Let your audience select food right on the website to make online orders with no redundant procedures. The only thing your staff will have to do is order confirmations.
- Using your customer base for promo campaigns: Collecting a database of loyal customers is crucial for the food delivery providers who are not going to rest on the ground. Tell your customers about special propositions via email and SMS campaigns, multiply reorders, send promo codes, offer bonuses. In other words, do what the industry leaders do using your customer base collected via your website.
- Introducing your service on the internet: Publish your service info on Google Maps, collect your customers’ feedback, use online marketing tools and the success won’t be long in coming.
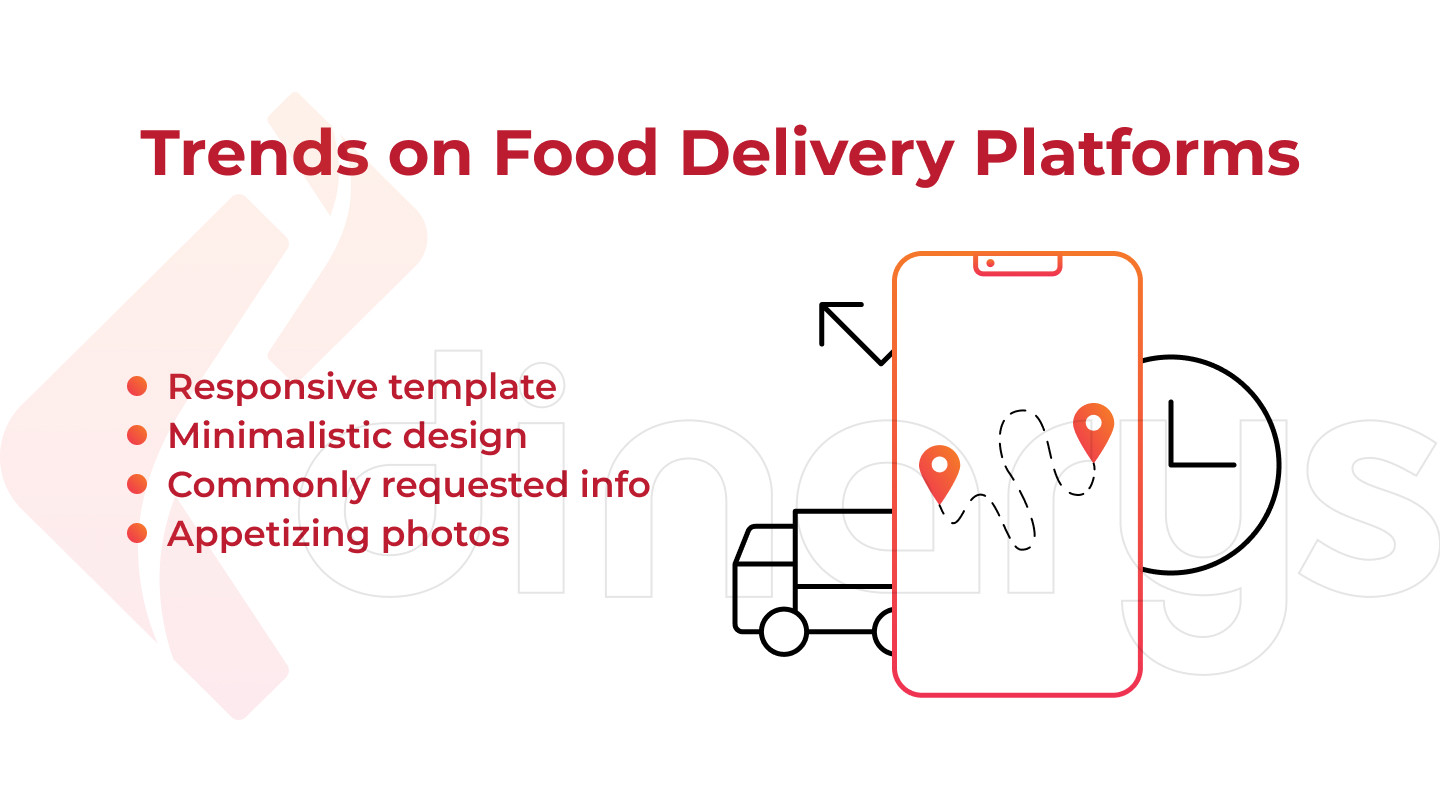
Common Trends on Food Delivery Platforms
A typical website of a food delivery service is a kind of interactive menu that provides customers with an opportunity to order food online. Both the architecture and design of such a website are determined by some current trends that have appeared not for nothing. It doesn’t really matter whether the trends reflect either the wisdom of crowds or natural selection between existing food delivery vendors. The important thing is that the trends help you mentally construct a viable prototype of your food delivery platform.
-
Responsive template: The one that looks equally great on both desktops (laptops) and mobile gadgets (smartphones, tablets) can make expensive mobile apps redundant.
-
Minimalistic design: Never let anything distract your customers from ordering food. Numerous pop-up windows can irritate customers damaging their user experience. Design is a critical factor since humans perceive reality mostly through their eyes. Even though visual elements constitute almost infinite space for creativity the following tips are worth keeping in mind while designing your food delivery website:
- The color scheme should be pleasant in appearance, not hassling. Remember that you create the platform for your clients, not for your own satisfaction. A white background seems to be universal, it simplifies working with pictures.
- Info about goods in the basket should be visible all the time. When customers scroll over the pages of your website the ordered goods along with their price should remain available on the screen.
- The “back to top” button should be available in the footer. You can rename the button however you like, but its function should be instantly graspable for users.
- Fix the main menu either on the top (it can save the space for other info) or on the left hand. The main menu should forward customers to the info pages such as delivery & payment terms, current campaigns, basket processing, etc.
- Don’t use heavy pictures. Slow downloading pages can frustrate your customers to make them leave your website. Optimize all graphic elements to provide page load faster.
-
Commonly requested info: The first rule of being a good website is displaying the most requested information on the main pages. The catalog, delivery & payment terms, customers’ feedback, current promo campaigns, and contact data constitute such important info inter alia.
-
Appetizing photos: Hire a professional photo stylist to create mouth-watering pictures of the food you offer. Remember that they are the main vehicle of sales in the online food delivery business.
Architecture & Functions
The entire functionality of your future food delivery platform depends on both the income-generating model and monetization strategy you have selected (see above). Not to bother you with all possible combinations of both aspects we propose considering an average variant with more or less full functionality. Let it be a service that covers a food delivery provider, independent couriers, and standalone restaurants. Such a structure implies having the three main sections of the website: for customers, couriers, and restaurant managers.
Functions for customers
This is the main and the largest section of a food delivery platform. The following features are a must-have for the section, therefore:
- Login page/registration form: The form should not be too detailed. Usually, customers do not want to spend more than 3 minutes filling the fields.
- Catalog of restaurants: A search bar, filters, and ratings should be available there in addition to a list of restaurants.
- Payment options: Banking cards, Apple Pay/Google Pay, and cash to a courier are the compulsory payment options for today. Add Bitcoin if payment in crypto is legal in your Country.
- Destination: There should be at least two elements there: a shared location integrated with Google Maps and an address bar to be filled manually.
- Basket/order processing: The feature should be interlinked with the main catalog to add goods to the basket automatically by clicking on the pictures.
- Customer support/chat with couriers: Both delivery instructions for couriers and customer feedback should be easily accessible for customers. Push notifications through integrated messengers can be a good option as well to keep customers informed about the current status of their deliveries.
- Order history: A reorder option should be available in a one-click mode.
Functions for couriers
This section is necessary when your food delivery service collaborates with standalone courier delivery providers instead of having your own courier team.
- Registration form: Both the courier company’s staff and independent couriers have to fill in the form to get access to your service.
- Order database: The list of current orders to be selected by couriers for delivery.
- Order status: It reflects whether the orders are ready for delivery, delivered, or pending.
- Order history: Total calculation of the delivery fees should be available there as well.
Functions for restaurants
The section serves the restaurant managers who have access to your platform.
- Admin panel for order processing: Restaurant managers should be able to control, process, and delete orders through the panel.
- Notifications for couriers: Either the on-site chat or push notifications via dedicated messengers can be used to notify couriers about the readiness of orders for delivery.
- Payment terminal: Restaurants should be able to print paychecks to send them together with the orders.
Website Structure
Everything we are indicating below is not a dogma, of course. This is the “classic” structure that can fit the majority of food delivery service platforms, as our experience suggests. The structure does not limit your creativity, however, especially when it comes to custom development.
-
Header: This is one of the most striking elements that often form the first impression from your website. Headers should not be overloaded with information. At the same time, this is the place where customers can easily find the most requested info:
- Your logo
- Working schedule
- Contact info (phone numbers, interactive social media icons, etc)
- Your location
- Links to info pages of your website
- Menu navigation
- Basket interactive icon
-
Home page: This is nothing but the face of your food delivery service. Try to make it as attractive as possible. Usually, the following info is displayed on the home page:
- Promo banners
- Your service advantages
- Compilations of the most popular goods
- Description of your delivery service
-
Food catalog: This is where your customers select goods to be added to the basket. It is worth dividing the displayed food into several categories. The following features are usually inherent in the section:
- Product cards with photos, brief descriptions, and price. Additionally, there can be the “add to basket” button on each card.
- The product card photo should be interactive: clicking on the photo should forward customers to a dedicated product page where they can find more detailed info on the product.
- Product filter through which customers can select a certain category of food with particular parameters. For example, they can select all gluten-free products.
- Additional navigation over other categories/pages for a simple transition between your website sections.
-
Product page: It contains full info on a product. This is what should be available there:
- Product picture
- Product name
- Price
- Brief and full descriptions
- Composition
- Weight
- Add to basket button
-
Basket: All selected products are displayed there. The following features should be available in the basket:
- Processing orders (deleting products, increasing/decreasing the number of each item, etc)
- Calculating the total price
- Adding promo codes/recalculating the total price
- Proceeding to checkout
-
Checkout: This is the purchase page where customers finalize their orders by adding their personal data to proceed with checkout. Payment gateways and fields for delivery details should be available there as well.
-
Support section: This section of your food delivery platform can combine several separate pages with different accessibility: some pages are for customers, the other ones are for your staff only. The scope of the section depends on the specific properties of your service (the income model, monetization strategy, business analytics, etc). The following features can be available on the pages:
- Customer support (an on-site chatroom, integrated messengers, etc)
- Delivery tracking
- Gift card/ loyalty program processing
- Sales analytics

Development Approaches
There are two main development approaches to the creation of your food delivery platform. The first one implies using appropriate frameworks such as Magento and Shopware. Another approach is individual custom development. Both approaches require professional developers, however. This is not because some special coding skills are necessary to work with Magento, for instance. But both the scope and complexity of a fully-fledged food delivery website leave not too much opportunity for amateur-made versions.
Framework-based development
The main advantage of the approach is the cost. It is significantly cheaper than custom development. If you have a limited budget while both the business idea and desired functionality of your future food delivery service do not go beyond the structure indicated above in the present post, your choice is framework-based development most likely.
Besides, already available capabilities, as well as the continuous evolution of Magento, provide customers with whatever they might wish to have in their projects. Almost any kind of bespoke tailor-made solution is possible to create with Magento development if true professionals take over. Magento marketplace opens up opportunities even further. A similar situation takes place with Shopware development as well. Both platforms are e-commerce-centric enough to allow various food delivery projects to see the light cost-effectively within a short time-to-market.
The final cost of each food delivery website is individual, of course. But the average price range of framework-based development is not a secret, nonetheless. It starts from approximately $6K with Shopware and from $15K with Magento. Magento marketplace is a little bit more expensive. Depending on the working hours spent for development, the cost of a food delivery website can unlikely go over $23K with Shopware and $25K with Magento. The exemplary food delivery project estimation can show a more detailed calculation.
Custom development
This is the most expensive approach. At the same time, only custom development can provide a literally unlimited extent of creativity along with unprecedented individuality for your project. It is fair to pay more for making your bravest dreams come true.
Custom development is worth doing when your project claims to be absolutely unique. An exceptional architecture, unparalleled functionality, copyrighted visuals all can impress your customers badly to occupy their attention once and forever. Quite significant investments in custom projects never remain without being compensated by larger profits and stronger sustainability. Don’t think twice if your financial capabilities allow you to order a custom food delivery platform.
The cost of custom development is very individual. Many factors affect the final figure. But our working experience suggests that a comprehensive multifunctional food delivery platform can be developed for $80k - 100K.
Summary: How to Create a Food Delivery Platform
The contemporary situation in the global restaurant market is definitely more than relevant to establishing food delivery services. A significant role of the recurrent lockdowns that have made millions of people adopt online purchasing is added by the never halting progress in the digitization of our everyday routines.
Answering the question of how to create a food delivery service we have mentioned almost every critical aspect that startup and restaurant owners should be aware of when getting down to the subject. The development of a food delivery website is not rocket science: it is easily graspable if software development professionals can assist in making proper decisions on such options as the income-generating model, monetization strategy, development approach, and the like.
Contact us today if a food delivery platform is your next project aimed at occupying a certain niche in the local catering sector. Magento, Shopware, and custom development are at your disposal with our experts who know exactly how a successful food delivery service should look and work.